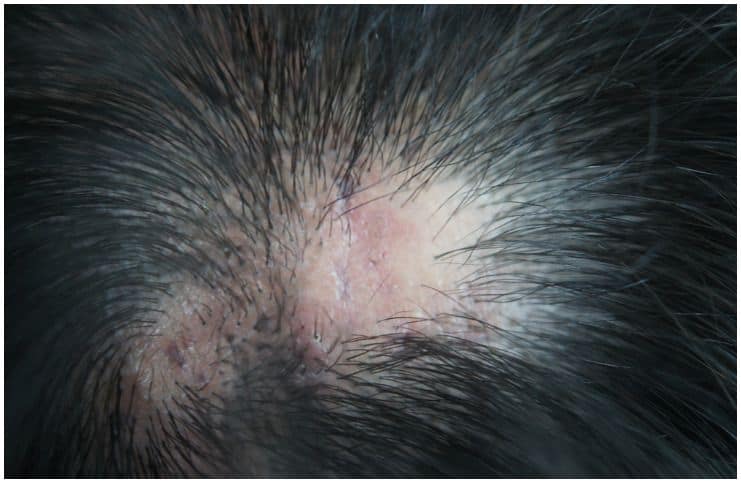
Lichen planopilaris, a type of lichen planus, is a rare inflammatory condition that results in patchy progressive and permanent hair loss mainly on the scalp. Three clinical variants of the condition can be classically observed – the Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome, the frontal fibrosing alopecia, and the classic form.
It is about 4 times more common in women than it is in men and is seen mostly in adults, with the most prevalent age of onset being in the mid-40s. Signs and symptoms may include:
- tiny, red pimples around clusters of hairs;
- patches of hair loss;
- burning, pain, tenderness, or itching on the scalp;
- redness and scaling around hair follicles.
Since hair regrowth in the bald areas is not possible in most patients, the goal of treatment is to stop the condition. Allopathic treatment may involve:
- hair transplantation;
- topical medicines, like – Tacrolimus or Clobetasol;
- injection of steroids into the affected area of the scalp;
- pills may be used, like – Plaquenil, Doxycycline, Mycophenolate mofetil, Isotretinoin (Accutane).
Here are the top home remedies and natural treatments for lichen planopilaris:
#1 Coconut Oil
Coconut oil has been used in Asia, Africa, and South America for centuries. Furthermore, it was used in American processed food in the middle part of the 20th century. Its unique combination of essential fatty acids can have positive effects on human health.
For instance, coconut oil not only soothes your itchy scalp caused by this condition but may also prevent it altogether. It has also been found to have an anti-inflammatory effect on skin and boost protective barrier functions.
To use coconut oil, just massage some coconut oil into your scalp and let it sit for awhile. Rinse the essential oil from your hair and shampoo as normal to remove the excess oil. This will help relieve the itchiness, plus, you will smell delicious.
#2 Castor Oil
Castor oil extracted from the castor seed (scientific name – Ricinus communis) is a potent oil that can reduce pain and works as a stimulant for the immune system. It can also be used as an antibacterial and anti-viral agent to treat several skin problems due to its unusual chemical composition.
It contains numerous nutrients, such as – omega-9 and 6 fatty acids, vitamin E, and proteins that give it unique moisturizing characteristics which are ideal for maintaining healthy scalp and hair.
#3 Oats
An oatmeal bath is a popular natural remedy to help alleviate the pain of rashes caused by chickenpox, poison ivy (caused by an allergic reaction to an oily resin called urushiol), and sunburns. Moreover, when applied to the scalp daily, it can help with inflammation associated with lichen planopilaris and psoriasis.
#4 Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a wonder plant that certainly should belong in every home and has been used for centuries on the skin to soothe and treat rashes, cuts, itching, and burns due to its high content of minerals and vitamins. As if all these were not enough, the amino acids in this fantastic plant facilitate the growth of healthy tissue and the enzymes in it also exfoliate the dead skin cells.
To use it, you can just spread some aloe vera gel onto the scalp using your fingers. Allow it to sit for twenty minutes and then wash the hair with a mild shampoo.
#5 Horsetail
Chinese, ancient Greeks, and Roman herbalists have been using horsetail (botanical name – Equisetum arvense) for its medicinal benefits. Moreover, because of certain minerals and enzymes, it contains, this medicinal herb may improve the health of your skin and hair.
#6 Yoga & Mindfulness Meditation
Strengthening and stretching exercises, along with mindfulness meditation (involves paying attention to the breath, and when your attention wanders – and it usually does -, return your attention to the breath) improve blood flow because they help reduce your stress levels.
Science also backs this. For example, a recent study concluded that individuals who practiced a daily mindfulness meditation-based stress reduction session healed quicker than people who didn’t.
#7 Tea Tree Essential Oil
It is a remarkable essential oil that has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. This means it has the capacity to fight viruses, bacteria, and fungus.
To use tea tree essential oil, you can dilute 3 drops of oil in a tbs of vegetable oil. Then, massage on the scalp and leave it on for about 2 hours. After, rinse your hair with mild shampoo and water. This will help unclog the hair follicles and get relief from itching. You can use this remedy once per week.
#8 Stinging Nettle
Stinging nettle is a flowering perennial plant that is native to Europe, North America, and Asia.
The most important health benefits of this plant include its capacity to detoxify the human body, enhance immunity, boost metabolic efficiency, and aid in skincare.
Massage stinging nettle essential oil into the scalp at night every second day.
#9 Baking Soda
It kills the harmful microbes on the scalp which are causing itchiness and infection due to its potent antibacterial and antifungal properties. Moreover, baking soda soothes the skin and neutralizes the pH of the scalp.
To use it, you can mix 2 tbs of baking soda with water and a few drops of olive oil (if you are not allergic). Then spread the mixture on the scalp and let it sit for 15 minutes. After, rinse your hair with mild shampoo and water. Repeat this procedure once or twice a week.
#10 Lemon Juice
Because of its antiseptic properties, it can help ease your itchy head. Lemon juice is also high in phytochemicals that have anti-inflammatory properties.
To use it, you can apply fresh lemon juice thoroughly on the scalp and let it on for 10 m. After, rinse your hair with mild shampoo and water.
Note – do not use lemon juice if the skin is broken because this may cause stinging.
Images credit -Shutterstock & Getty
READ THIS NEXT: Postherpetic Neuralgia – 10 Home Remedies
References https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/711925 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3470848/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4631232/ http://c.ymcdn.com/sites/www.aocd.org/resource/resmgr/jaocd/contents/volu