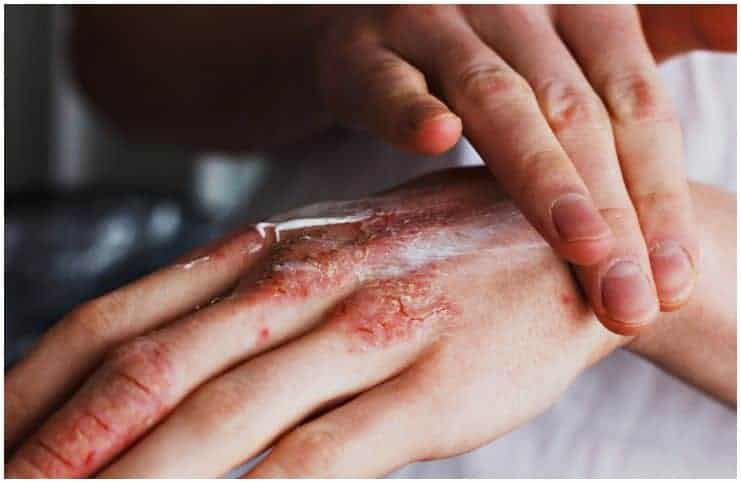
Scabies vs Eczema – detailed comparison:
Scabies
It is a skin condition caused by an infestation by the itch mite (scientific name – Sarcoptes scabiei).
The mite can survive for 3 to 4 days without being on a human.
Untreated, these mites can live on your skin for months.
They reproduce on the surface of the skin and then burrow into it and lay eggs (the mites which infest humans are female and are 0.3 mm-0.4 mm long).
This causes an itchy, red rash to form on the skin.
The scabies rash typically spreads across the whole body – apart from the head.
These mites like warm places, like – between the fingers, skin folds, under fingernails, or around breast creases or the buttock.
More than 300 million people are infected every year worldwide, including 1 million people in the US.
This skin condition is highly contagious and can spread from person to person through close physical contact. Institutions, like extended-care facilities, nursing homes, and prisons, are common sites of scabies outbreaks.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms include:
- intense itching that is usually worse at night, and it can involve any part of the skin;
- thick crusty skin;
- sores;
- tiny blisters or bumps on the skin;
- reddish scratched skin which itches.
Complications
Vigorous scratching can break the skin and allow a bacterial infection, like – impetigo, to occur.
Furthermore, in sufferers who are malnourished or who have poor immune systems, these mites can cause Norwegian scabies, which is highly contagious and is associated with a scaly rash and skin thickening.
Causes
This condition is caused by an eight-legged mite that is less than 0.5 mm long. It is typically spread through prolonged periods of skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. The skin-to-skin contact needs to be for 15 to 20 minutes.
Mites can live for 2 to 3 days in bedding, clothing, or dust, making it possible to catch the condition from individuals who share the same infected linens, bed, or towels.
Note – pets are infested with different types of mites than those that infect humans. Therefore, pets are not a source of spread of human scabies.
Risk Factors
Factors leading to spread of the condition include:
- lack of proper treatment of the disease;
- low rates of identification;
- having a weak immune system;
- living in refugee camps, hospitals, institutional care, or prisons.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider will likely be able to diagnose the condition simply by inspecting the affected area of the skin.
To rule out other dermatoses (diseases of the integumentary system), mites are identified with the help of a biopsy.
Treatment
The main treatment of affected people involves an application of a topical scabicide, like – 5% malathion in an aqueous base, permethrin 5%, or 5–10% sulfur ointment.
Natural remedies, like – tea tree oil and cayenne pepper, are proven to help to eliminate a scabies infestation and reduce pain.
Eczema
It is not a single health condition, however, it is a recognizable reaction pattern seen in many different skin diseases. It can cause symptoms including blisters, redness, crusting, oozing, thickened skin, scaling, and pigmentation changes.
There are at least 10 distinct types of skin conditions that produce eczema, including atopic dermatitis, irritant dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, fungal infections, pompholyx, lichen simplex chronicus, nummular eczema, xerotic (dry skin) eczema, or seborrheic dermatitis.
The most common cause of eczema is atopic dermatitis. About 20 percent of children develop atopic dermatitis, commonly in infancy and generally by age 5. The condition is harder to control in arid areas in the wintertime and is less common in very humid environments.
READ MORE: Folliculitis vs Herpes
Symptoms
The main symptom is itching, which can lead to rubbing and scratching, which further inflame and irritate the skin.
Other symptoms include:
- ear discharge or bleeding if eczema occurs in the ear canal;
- leathery patches of skin from chronic scratching;
- skin color changes;
- hives, especially after exposure to an allergen or after taking a hot shower;
- skin which is sore and swollen;
- increased skin creases on the palms of the hands;
- blisters or papules which crust over when scratched;
- scaly skin patches, which may be red and rectangular;
- rough bumps on the upper arms, face, and thighs;
- patchy loss of eyelashes or eyebrows from rubbing or scratching;
- an extra fold of skin that develops under the eye.
Causes
While the precise cause of eczema is unknown, doctors believe it is a product of the environment and genes.
READ MORE: Balanitis – home remedies
Risk Factors
Risk factors include:
- ADHD;
- a family history of hay fever, eczema, or asthma;
- living in a dry climate;
- emotional stress;
- young age;
- low vitamin D levels during pregnancy;
- adolescent obesity, for later onset of eczema cases;
- nutritional deficiency and unhealthy diet;
- lack of sleep;
- regular contact with chemicals, harsh soaps, skin care products, and perfumes that contain alcohol or fragrance.
READ MORE: Essential Oils For Lichen Sclerosus
Diagnosis
A dermatologist will base his diagnosis on a physical examination and detailed medical history.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to prevent and relieve itching, which can lead to skin infection and damage. Treatments include:
- antihistamines may help the itching;
- corticosteroids reduce the inflammation in response to an allergic reaction;
- phototherapy may also improve acute eczema.
Scabies vs Eczema – Differences
Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. Classic scabies usually manifests as an intensely pruritic eruption with a characteristic distribution. It is spread by direct, skin-to-skin contact with an individual who has scabies. Contact must be prolonged; a hug or a quick handshake will not usually spread scabies.
Eczema is a term for a group of medical conditions which cause the skin to become irritated or inflamed.
In conclusion, these diseases are completely different in terms of cause, spread, and treatment.
READ THIS NEXT: Monk Fruit vs Stevia
References https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22726646 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7829652 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4751955/