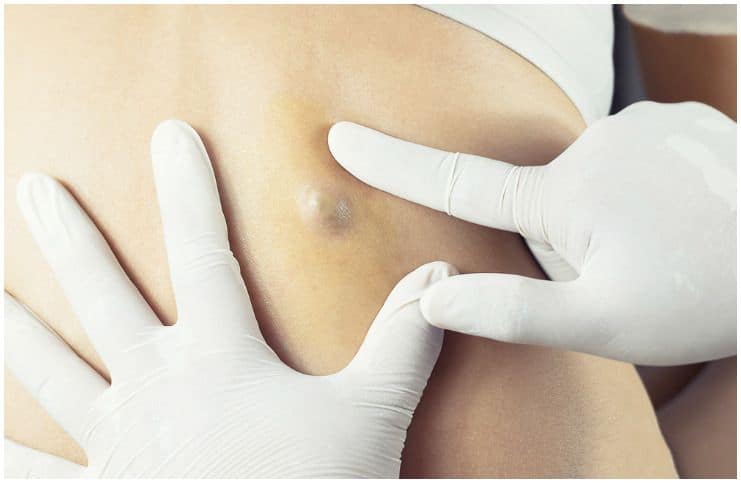
Sebaceous Cyst vs Lipoma – Differences:
Sebaceous Cyst
It is a noncancerous lump behind the ear, that develops underneath the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body, however, it is usually found on the neck, face, and torso.
Additionally, it has a size measuring up to a few centimeters, and it is very slow-growing.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- yellow, thick, foul-smelling substance draining from the lump;
- a blackhead plugging the central opening of the cyst;
- infection or inflammation;
- swelling, redness, tenderness;
- a small, round lump under the skin.
Complications
If the cyst ruptures, you will need treatment right away since it can lead to a boil-like infection.
Causes
It occurs when a hair follicle is ruptured or swollen, either due to an injury to the skin, acne, or a sebaceous duct that is malformed.
It may also be caused by swollen hair follicles in the skin as well as trauma to the skin.
Other causes of a sebaceous cyst may include:
- genetic conditions, like – basal cell nevus syndrome or Gardner’s syndrome;
- damage to the cells during surgery.
Risk Factors
Some of the risk factors include:
- forcefully pulling out a strand of hair;
- an injury to the skin;
- certain genetic disorders;
- having a prior history of acne;
- adolescence.
Diagnosis
Common tests used for a sebaceous cyst include:
- punch biopsy;
- ultrasounds;
- CT scans.
Treatment
Sebaceous cysts are commonly treated by draining the fluid and removing the shell which makes up the cyst wall.
Home remedies include:
- antifungal creams – applying the cream to the infected area can reduce the symptoms;
- turmeric – use half a tsp of turmeric powder added to one cup of warm water;
- bee pollen – consume bee pollen as it purifies the blood;
- Epsom salt – it can be used in a warm bath to help draw the infection out of the cyst;
- black blood root drawing salve – it can be applied to a salve on the lump;
- apple cider vinegar – it can be effective if a cyst has become infected;
- castor oil – it helps reduce any itching and inflammation associated with the lump;
- aloe vera – it can help if the cyst is irritated or inflamed due to rubbing up against something;
- tea tree oil – it has been known to reduce the reoccurrence of sebaceous cysts as well as protects the cyst against infection due to the fact that it has both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Lipoma
A lipoma is a fatty lump that is most commonly located between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. Healthcare providers think that lipomas are benign tumors, meaning that they are non-cancerous growths. Cancerous tumors of the fat cells are called liposarcomas.
A lipoma can form on any part of the body, however, they usually appear on the:
- thighs;
- neck;
- arms;
- shoulders;
- abdomen;
- back.
It can develop in people of any age, even in newborns, however, it usually occurs in adults between ages 40 and 60. Approximately 1 in 100 people will develop a lipoma during their lives. They usually occur on one side of the body. Lipomas rarely grow more than three inches across.
Subtypes:
- superficial subcutaneous lipomas – they mostly grow on the forearm, trunk, and thigh and occur just below the skin surface;
- pleomorphic lipomas – they occur mostly in seniors males;
- spindle cell lipomas – they are mostly seen in seniors males on the posterior of their shoulders, back, and neck;
- neural fibro-lipomas – a rare subcutaneous benign lesion;
- intradermal spindle cell lipomas – they usually occur in parts such as the trunk, neck, head, and extremities;
- chondroid lipomas – they characteristically grow on the legs of females;
- hibernomas – these are the lipomas of brown adipose tissue;
- angiolipoleiomyomas – these are solitary, asymptomatic acral nodules;
- angiolipomas – these are the painful subcutaneous nodules;
- adenolipomas – these are associated with the eccrine sweat glands.
Symptoms
Common characteristics:
- slow growth;
- soft to the touch;
- colorless;
- pale;
- they occur just under the skin;
- they move easily if prodded with your finger.
READ MORE: Petechiae vs Purpura – Causes & Differences
Causes
The causes of lipomas are unknown. But, there are possibilities that they are caused by any physical trauma to the specific part of the physical body.
Additionally, genetic factors play a substantial role in the development of lipomas.
Risk Factors
The following factors may increase the risk of developing a lipoma:
- genetics as lipomas tend to run in families;
- having other disorders, such as – Cowden syndrome, adiposis dolorosa (a condition that is described by fatty tumors in the adipose tissue), and Gardner’s syndrome;
- age between 40 and 60 years.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider may perform one or all of the following exams:
- imaging tests, like – MRI, ultrasound, or CT scan;
- removal of a sample of tissue for microscopic examination;
- physical exam.
READ MORE: Fregoli Syndrome vs Capgras Syndrome
Treatment
Treatment of lipomas is not commonly required, however, some lipomas may be removed by liposuction (during which a needle and a large syringe are used to remove the fatty lump) or by surgery.
A lipoma is only removed when:
- it is suspected to be a cancerous tumor and must be removed for diagnosis;
- you may want to have your lipoma removed for cosmetic reasons;
- it is in an area where recurrence could be dangerous;
- your lipoma is causing symptoms, for instance, by blocking the bowel or by pressing on a nerve;
- your lipoma is growing larger.
READ MORE: Choroideremia vs Retinitis Pigmentosa – Symptoms & Differences
Bottom Line – Sebaceous Cyst vs Lipoma
A sebaceous cyst is a slightly hardened, fluid-filled bump within the skin. The main symptom of a sebaceous cyst is a small lump under the skin. Commonly, a sebaceous cyst doesn’t cause pain and grows very slowly.
A lipoma is a growth of fatty tissue that slowly develops under the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body where fat cells are present, however, a lipoma tends to appear on the chest, trunk, shoulders, thighs, neck, and armpits. A lipoma is not cancer and is typically harmless. Also, you may be able to move a lipoma around a bit and it feels rubbery.
The main difference is that a lipoma is usually found more deeply beneath the skin, whereas a sebaceous cyst tends to be closer to the skin’s surface.
READ THIS NEXT: Tuberculoid vs Lepromatous Leprosy
References https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289923278_Sebaceous_cyst_-_A_case_study https://www.journal-surgery.net/article/S1743-9191(16)30604-5/fulltext https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/17453054.2011.579896?journalCode