Magnesium glycinate is one of the most absorbable forms of magnesium, with minimum risks of causing diarrhea.
This supplement is water-soluble and is absorbed via a mechanism similar to that used by amino acids, hence, it is not dependent on stomach acid for absorption. Doctors usually recommend it to patients who are seeking to raise their magnesium serum levels fast.
Deficiency
Many factors contribute to magnesium deficiency, such as – prolonged stress, irritable bowel syndrome, thyroid problems, or kidney diseases.
Signs of a deficiency include – impaired memory, lethargy, seizures, sleep disorders, fatigue, muscle cramps, headaches, chronic back pain, migraines, tendonitis, muscular pain, aggression, ADHD, and anger.
Health Benefits
Supports bone health
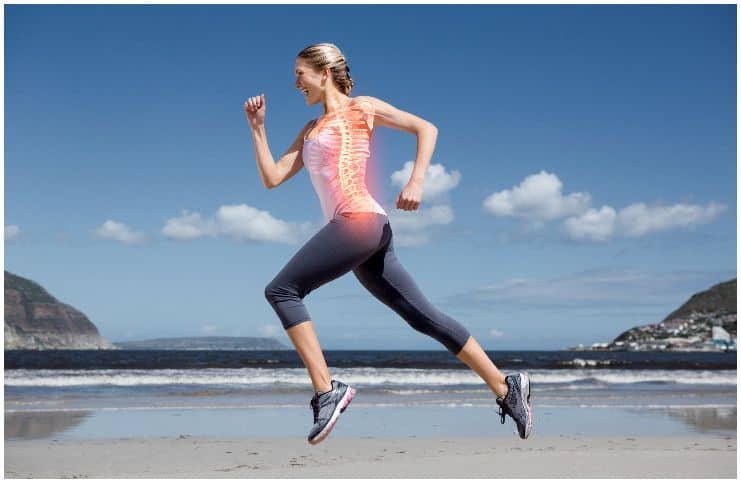

However, in order for calcium to properly assimilate into the human bone structure, a proper balance of both magnesium and vitamin D is important.
Promotes healthy sleep
This mineral found in numerous foods is a crucial component of more than 300 types of enzymes in the human body and plays an important role in the quality of sleep.
This may be because the body needs this mineral to maintain a state of rest and a lack of it can lead to restless muscles that can keep you awake at night.
Remineralizes teeth
Our bodies store over 60 percent of it in teeth and bones. Many studies have established that cavity-free teeth have mineral levels of 100 percent, unlike teeth with cavities.
Anxiety
Patients with anxiety have been found to have lower levels of this mineral which may be strongly associated with the fact that a deficiency causes the release of adrenaline (a hormone released from the adrenal glands).
In addition, glycine is acknowledged as a calming amino acid, especially when it’s combined with this mineral. According to a 2012 study at the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Innsbruck, Austria, patients who received this supplement were able to reduce their anti-anxiety prescription drugs and symptoms of anxiety disappeared.
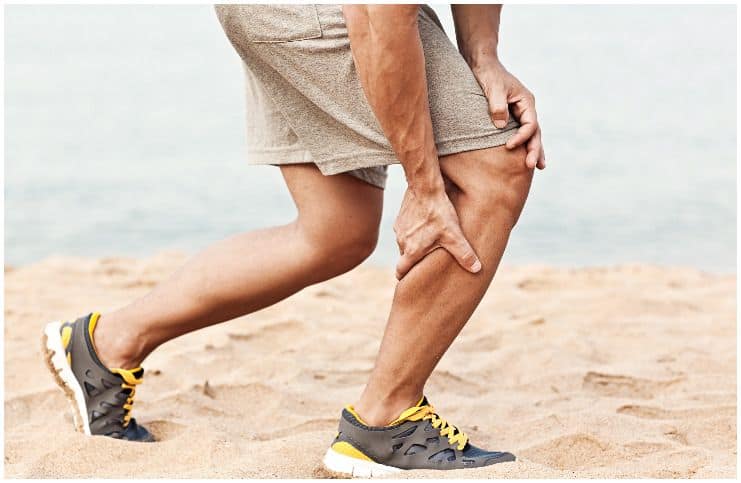
Muscle weakness and cramps
It is closely involved in proper muscle contraction and relaxation. Athletes can be particularly prone to more loss from sweating. This supplement allows the body to produce more IGF-1 – an insulin-like growth factor that is an important contributor to the strength and growth of muscles.
Heavy metals
Heavy metal toxicity can disrupt the brain chemistry causing anxiety and depression, and can also considerably weaken immunity. This mineral plays a key role in the body’s detoxification processes, especially heavy metals and other toxins.
Recommended daily allowance
Birth to 6 months: 30 mg
7–12 months: 75 mg
1–3 years: 80 mg
4–8 years: 130 mg
9–13 years: 240 mg
14–18 years: 360 mg for women; 410 mg for men
19–30 years: 310 mg for women; 400 mg for men
Adults 31 years and older: 320 mg for women; 420 mg for men
Women who are breastfeeding: 310-320 mg
Pregnant women: 350-360 mg
Note – according to statistics, about 57 percent of the United States population does not meet the minimum RDA.
Side Effects Of Magnesium Glycinate
Individuals who have kidney problems should consult a healthcare professional before taking this supplement. If they consume too much, they may experiment stomach upset or loose stools due to the very stable chelate formed between each magnesium ion and the two glycine molecules.
In addition, common signs of excess magnesium include stomach cramps, changes in mental status, muscle weakness, nausea, difficulty breathing, diarrhea, loss of appetite, irregular heartbeat, and extremely low blood pressure.
List Of Magnesium Rich Plants
Plant sources of this mineral include:
- Fruits – bananas, tamarinds, figs, prickly pears, peaches, prunes, apricots, dates, roselle, longans, litchis, currants, plums.
- Whole grains – quinoa, buckwheat, millet, bulgur, barley, wild rice, oats.
- Leafy vegetables – spinach, collard greens, swiss chard, kale, turnip greens.
- Beans – lentils, French beans, soybeans, white beans, kidney beans, black-eyed peas, chickpeas, pinto beans.
- Nuts – almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, peanuts, pine nuts, pecans, walnuts.
- Seeds – sesame seeds.
What this video about top plant-based foods high in magnesium.
References https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3198864/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23853635 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19488681?dopt=Abstract




Please email me information related to this issue of deficient magnesium symptoms (I now suspect this as underlying many if not most of my mysterious birth defects) and the symptoms of excess magnesium glycinate supplementation symptoms which I am currently battling after overdosing magnesium glycinate and Milk of Magnesium to dislodge constipation stuck for days for the first time in my life and several times in a row. Never suspected it until I saw that it does not dissolve in water at room temperature. I fear I may have really thrown myself off balance with all the mysterious symptoms of too much in my system at this time.
I’m glad to find a related cause, but not sure how to correct it. I’ve stopped taking any more but everything tastes like soap still and makes me queasy including water and I’m getting dehydrated. I need more informed advice regarding this particular mineral. Oh yes I have no appetite and can’t sleep,
Not good – scary.
Please advise at [email protected]
Thank You.