Famotidine
It is an oral drug that belongs to a class of drugs called H2 (histamine-2) blockers which block the production of acid by acid-producing cells in the stomach.
This drug is typically used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (a condition in which backward flow of acid from the stomach leads to injury of the esophagus and heartburn) and peptic ulcer disease (painful sores in the lining of the stomach).
It is available as a brand-name drug (Pepcid, first marketed in 1981) and as a generic drug (a drug that has exactly the same active ingredient as the brand-name drug, but cheaper).
The prescription form is commonly used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease, ulcers, erosive esophagitis (due to chronic GERD), and other conditions. The over-the-counter form is used to prevent and treat acid indigestion, heartburn, and upset stomach.
Moreover, this medicine is found in an injectable form, that is only given by a doctor and a liquid suspension, which you may take by mouth.
Dosage
Each tablet for oral administration contains either 20 mg or 40 mg of this drug and the following inactive ingredients – hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, iron oxides, corn starch, microcrystalline cellulose, titanium dioxide, talc, and carnauba wax.
To treat erosive heartburn, adults can take 10, 20, or 40 mg two times a day. To treat gastroesophageal reflux disease, adults can take 20 mg two times a day.
To treat stomach ulcers, adults can take 40 mg once a day at bedtime or 20 mg one or two times a day.
This medicine may be only part of a complete program of treatment which also includes changes in lifestyle habits and nutrition.
For instance, certain drinks and foods may make heartburn worse, including – spicy food, greasy/fried food, carbonated drinks, citrus fruits, and alcoholic beverages.
Uses
It is usually used for conditions like – duodenal ulcers (ulcers of the upper part of the intestine), gastric ulcers (stomach ulcers), indigestion, and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (heartburn).
Also, it treats conditions in which the stomach produces too much acid, especially the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Although the FDA does not approve this medicine for veterinary use, veterinarians do frequently give the drug to cats and dogs to reduce stomach acid if they are producing too much.
Side Effects And Precautions Of Pepcid
Common side effects include:
- vomiting;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- nausea;
- dry mouth;
- joint pain;
- muscle pain;
- insomnia;
- headaches;
- mood changes;
- weakness;
- dizziness.
Drug Interactions
If you are taking this drug for self-treatment, it is crucial to read the manufacturer’s package instructions properly. This drug may interact with itraconazole, atazanavir, ketoconazole, or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Pregnancy & Breastfeeding
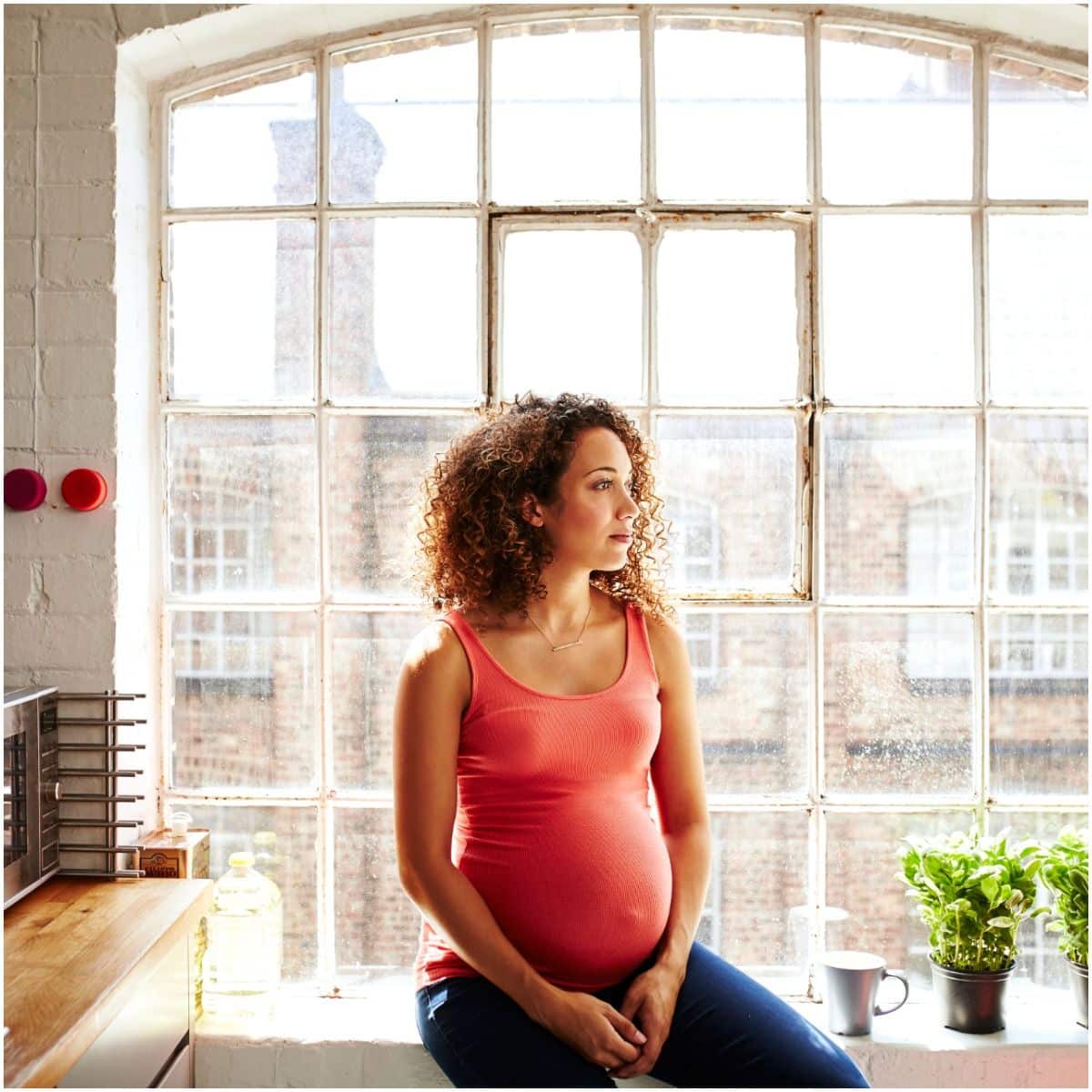

If you are breastfeeding, before taking this medicine, it is recommended to discuss it with your healthcare provider, since according to studies, it is secreted into breast milk.
Additionally, the safety of the H2 (histamine-2) blocker has not been established in suferrers with arthritis receiving nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the long term.
Ranitidine
It belongs to a group of medicines called H2 – blockers or H2 – antagonists. Its over-the-counter form is used to treat conditions where a reduction of stomach acid is required, like – heartburn, acid indigestion, or upset stomach.
Uses
It is used to reduce the amount of acid secreted by the stomach in order to assist in the healing of ulcers or to alleviate heartburn symptoms since gastro-oesophageal reflux can cause a painful burning sensation in the chest rising as well as an unsettled stomach.
This drug can also be used to treat children as young as one month old. Before using this medicine on a child, you should talk to your doctor since the use of this drug in infants is linked with a higher chance of NEC (necrotizing enterocolitis), infections, and fatal outcome in VLBW infants (very low birth weight infants).
It is sometimes used in cats and dogs to prevent and treat ulcers of the esophagus and gastrointestinal tract.
Side Effects And Precautions
Side effects may include:
- difficulty in breathing;
- muscle pain;
- mental confusion;
- stomach pain;
- diarrhea;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- headaches.
Individuals who already have symptoms of a decreased liver function should use this drug with extra caution since cases of hepatitis caused by using this drug have also been reported.
Also, if you have kidney disease, you should not use the over-the-counter form, unless you are under the advice of your doctor.
Alcohol
To prevent side effects, do not intake alcoholic beverages while taking this medication.
Famotidine vs Ranitidine – Which Is Better For Heartburn Relief?
Although they are distinct drugs, by interfering with specific receptors on the outside of stomach cells, they reduce acid production by the cells which line the stomach with almost similar outcomes.
For instance, during a 24-week observation in 1991 at Gastrointestinal Unit, Milan, Italy, the relief of day and night pain was reported by 73.5 percent and 85.5 percent of the ranitidine (Zantac)-treated sufferers, respectively. The corresponding figures in the famotidine group were 81.2 percent and 91.8 percent.
Furthermore, Zantac is usually preferred over other H2 receptor antagonists for use during pregnancy. Also, according to data, the overall incidence of adverse effects observed with the use of these drugs appears to be similar.
Images credit – Shutterstock & Getty Images
READ THIS NEXT: Pantoprazole vs Nexium
References https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02772241003636505 https://gut.bmj.com/content/gutjnl/29/1/81.full.pdf https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199605303342204