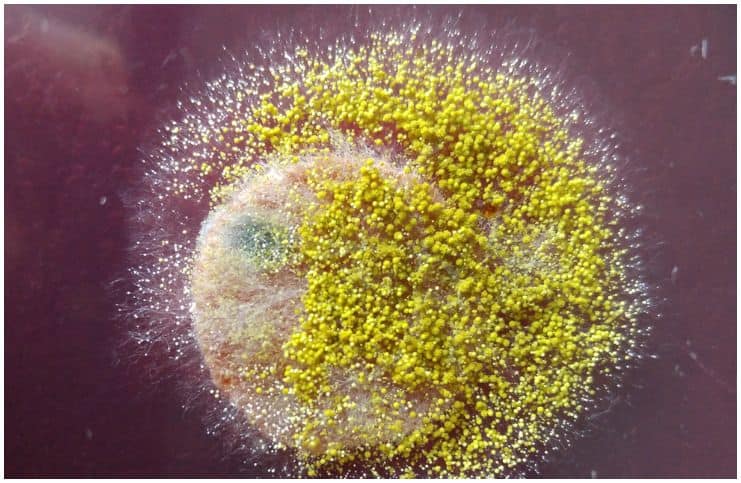
Aspergillus and penicillium molds have a particular environmental importance. However, the main problem with this fungus in agriculture is that it produces a very carcinogenic type of toxins, named – aflatoxins that are a considerable hazard to animals and humans.
Aflatoxins, that are well known to be carcinogenic, mutagenic, immunosuppressive, and hepatotoxic, exert inhibitory effects on biological processes including DNA-dependent RNA synthesis, DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and DNA repair.
In the field, Aspergillus flavus is mainly a problem in the oilseed crops maize, cottonseed, peanuts, and tree nuts.
About 16 species of A. molds are known to have adverse to humans, causing infection and disease. For instance, it is the 2nd leading cause of aspergillosis in humans.
These saprophytic heterotrophic organisms belong to the category of decomposers, helping nature dispose of organic wastes, such as lignin and cellulose.
We must mention that nature doesn’t produce non-biodegradable waste, according to an environmental law, which states that:
“for each biosynthesized substance, nature has created an enzyme capable of degrading it.”
In other words, we must thank these molds for the fact that we don’t live buried under tens of meters of natural and human waste.
A. flavus, like other species belonging to the genus Aspergillus, is a heterotrophic, saprophytic fungus, which is often found in nature.
Due to the fact that it breaks down cellulose and lignin, the fungus has a special ecological value. Sometimes, in certain circumstances, it can become an optional parasite organism for plants, animals or humans.
Fungi attack mainly the cellulose and lignin sublayers (straw, corn cobs, peanuts, nuts, wood, etc.) and from here, by eating them, they reach the body of animals and humans. Only secondarily, mold spores can enter the body through the air.
But even in these conditions, it rarely manages to grow and multiply inside these organisms as a parasite (a defense mechanism that manages to destroy and eradicate these spores).
Dangers of Aspergillus Flavus
In humans, in rare cases, it can continue its life cycle inside the body as a pathogen. Sometimes it locates cephalic, causing intracranial aspergillosis, a severe illness that is often lethal. In general, aspergillosis occurs in immunocompromised patients or farmers, in which case spores are localized mainly in the paranasal sinus.
In order to avoid the negative effects of mold and not expose ourselves, it is recommended not to eat nuts or peanuts which are beginning to alter, changing their taste and smell, or those growing rancid.
Aflatoxins can be found in coffee, peanuts, corn, hazelnuts, and spices that are stored in improper conditions.
Furthermore, the toxin cannot be destroyed by boiling (cooking) or metabolism. Thus, an animal that has eaten infected corn can transmit the toxin to humans eating its meat.
Reference https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20507532