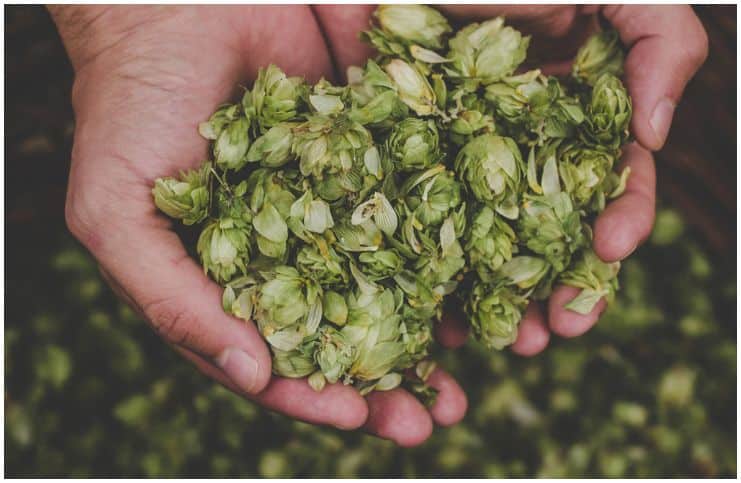
Hops (Humulus lupulus): Side Effects and Health Benefits:
Hops or hop (Humulus lupulus) is a climbing vine belonging to the genus Humulus in the family Cannabaceae, frequently trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden (nomenclature in the south of England), or hop yard (in the United States and West Country) when grown commercially.
The origin of the Hop genus’ name, Humulus, is considered doubtful, though it has been considered by some writers that it is derived from humus, the rich moist ground in which the plant grows.
The precise name ”Lupulus” is derived from the Latin lupus (wolf) because, as Pliny explains, when produced among osiers, it strangles them by its light, climbing embraces, as the wolf does to a sheep. The English name Hop comes from the Anglo-Saxon hoppan (to climb).
In Europe, this plant is cultivated in Great Britain, Germany, the Czech Republic, and Poland. In Asia, cultivation takes place in certain areas of China and, to a limited extent, in Japan.
For the Southern Hemisphere, cultivation of Humulus lupulus occurs in New Zealand from 41º to 42º and in Australia from 37º to 43º latitude.
In what forms can we take it?
We can take it in different ways, including capsules, dried as an herbal tea, as a tincture (a medicine made by dissolving an herb in alcohol), in tablets, in lotions, and in creams.
Health benefits of Hops (Humulus lupulus)
The female flowers of the plant are commonly used to treat fibromyalgia, arthritis, insomnia, diabetes, and menopausal symptoms.
Additionally, in Indian-Ayurvedic medicine, this herb has been recommended for restlessness connected with headache, nervous tension, and indigestion.
Cancer
Acids in the herb, called lupulones and humulones, have been shown to kill cancer cells and block leukemia cells from clinging to a bone in petri dish experiments. They may also act as anti-inflammatory compounds.
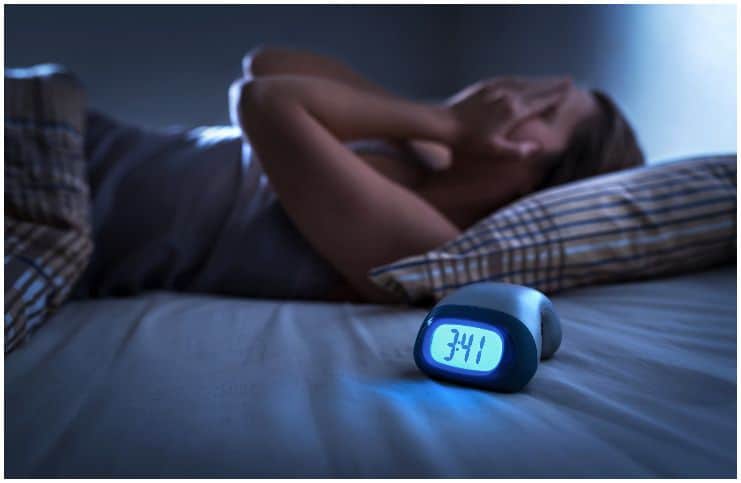
Insomnia
Pairing valerian with hops may help treat insomnia, according to a 2010 research review published in Australian Family Physician.
The review included 16 previously published kinds of research, 12 of which found that the use of valerian (Valeriana officinalis) on its own or in combination with Humulus lupulus helped improve the overall sleep quality and lessened the amount of time it takes to fall asleep.
While Valeriana officinalis can cause moderate side effects, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health notes it’s generally safe to use for short periods of four to six weeks.
Hair health
When used in combination with other natural oils on the hair, Humulus lupulus essential oil can improve the strength and sheen of the hair thanks to its potent volatile substances that interact with hair follicles and natural oils to improve the appearance and health of your hair.
Anti-Inflammatory properties
In a study published in the Molecular Nutrition and Food Research Sept 2009 issue, it was reported that Humulus lupulus bitter acids efficiently block inflammation independent of PPARalpha, GRalpha, or PPARgamma.
The study established the anti-inflammatory effect of various classes of hop bitter acids (HBA), including beta-acids (BA), alpha-acids (AA), and iso-alpha-acids (IAA), in fibroblasts, which are essential compounds in the inflammatory response.
Reduces menopausal symptoms
This plant also appears to have estrogenic effects. Extracts have been shown to reduce menopausal symptoms, and in one study with 100 postmenopausal women, a vaginal gel containing hops reduced painful intercourse, vaginal dryness, itching, burning, and inflammation.
Nevertheless, the study was not designed to distinguish between the effects of Humulus lupulus and other components of the gel, including vitamin E and hyaluronic acid (also called hyaluronan).
It may reduce joint swelling
A study published in the International Society for Horticultural Science reports that various hop extracts are powerful in inhibiting inflammation.
More research is needed, but many experts claim these herb extracts are a good joint-support product and show potency against osteoarthritis pain.
Contains phytoestrogen
Scientists from King’s College, UK, identified a potent phytoestrogen in this herb, 8-prenylnaringenin (also known as flavaprenin), which has an activity greater than other established plant estrogens.
Flavaprenin competed strongly with 17ss-estradiol for binding to both the alpha- and ss-estrogen receptors. This potent phytoestrogen can also be detected in beer containing hops, but the levels are low.
Side effects of Hops (Humulus lupulus)
The herb is not recommended for breastfeeding and pregnant mothers. Moreover, handling of this plant may cause skin rashes (allergies), breathing difficulties, and dry cough.
In serious cases or overdoses, its side effects may include hyperthermia, seizure, restlessness, stomach disturbance, and vomiting. It is unclear how intake of Humulus lupulus alters hormone-sensitive conditions such as certain kinds of cancers.
Although this plant has sedative effects, it is not recommended for administration to children and infants. If you are taking any prescription drugs, talk to your healthcare specialist before using hops.
Note
Most studies on hops use either supplements or non-alcoholic beer containing hops. Drinking too much alcohol can actually raise your risk of many chronic health conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, liver disease, and certain kinds of cancer.
READ THIS NEXT:
Garcinia Cambogia Side Effects
Green (Raw) Coffee Bean Extract Chlorogenic Acid Side Effects
Lifestyle Changes To Prevent Stroke
References http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1852439/