This article reveals the differences between contact dermatitis and scabies:
Contact Dermatitis
It is a rash which occurs at the site of exposure to a substance capable of producing an irritant or allergic skin response.
Scabies
It is caused by scabies mites, insect-like parasites which infect the top layer of the skin.
These mites are spread by sharing clothing, bedding, or towels with an infected person or via skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
An estimated 300 million cases are reported worldwide each year.
The highest rates occur in communities where poverty and overcrowding coexist and in countries with tropical climates.
The areas of the body most affected by scabies are:
- the folds under the arms;
- the inner part of the wrists;
- the hands and feet (particularly the webs of skin between the toes and fingers).
Symptoms
Contact Dermatitis
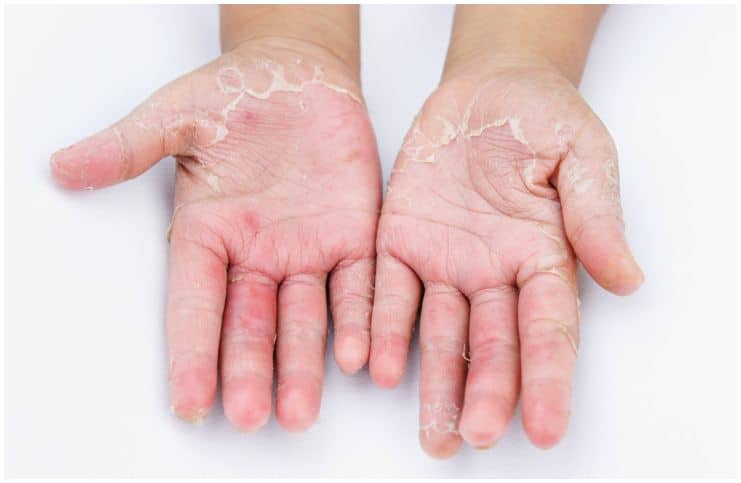
Common symptoms may include:
- swelling, burning or tenderness;
- bumps and blisters, occasionally with crusting and oozing;
- dry, cracked, scaly skin;
- itching, that may be severe;
- a red rash.
Scabies
Common symptoms include:
- very itchy bumps on the labia or scrotum;
- small, clear, fluid-filled spots or lesions;
- a bumpy or pimple-like rash that is commonly difficult to see;
- visible burrows in skin creases like genitals and armpits;
- visible burrows on the skin between the fingers;
- intense itching, usually worse after a hot bath or shower or at night.
Note – itching starts within 1 to 5 days in people previously exposed and approximately 2 to 6 weeks after infestation in people not previously exposed to the mites.
Complications
Contact Dermatitis
If the symptoms of contact dermatitis are severe or cause scarring, they can affect the quality of life.
Another possible complication is lichen simplex chronicus, a skin condition that causes chronic scaling and itching.
CD can also become infected with bacteria, commonly Streptococcus and Staphylococcus.
Scabies
Norwegian scabies may occur in individuals with a low immune system due to:
- severe nutritional deficiency;
- immunosuppressive medications treatment;
- chemotherapy;
- leukemia (a broad term for cancers of the blood cells);
- HIV infection.
Causes & Types
Contact Dermatitis
There are 2 types of CD:
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) – is a form of dermatitis that is caused by an allergic reaction to a material when in contact with the skin. Adults are most commonly affected by ACD; however, it can affect persons of all ages.
Allergens that usually cause ACD include the following:
- some plants, like – sunflowers, daffodils, chrysanthemums, tulips, and primula;
- cosmetic ingredients, including – fragrances, hair dye, preservatives, and nail varnish hardeners;
- strong glues, like – epoxy resin adhesives;
- textiles, especially the dyes and resins which are contained in them;
- rubber, such as – latex, a type of naturally occurring rubber;
- some topical medications, especially topical corticosteroids;
- metals – like – cobalt or nickel. Nickel may be found in the metal of watch straps, costume jewelry, jeans studs, and bra clips. The prevalence of nickel allergy is higher among females than males. An estimated 8 percent of the population is allergic to nickel.
Irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) – occurs at the site of the application of a toxic substance or chemical that is directly noxious to the skin. The skin can take up to 48 to 96 hours to develop an allergic reaction.
Common irritants include:
- many plants, like – spurge, Boraginaceae, Ranunculus, and mustards;
- detergents and soaps;
- water – especially heavily chlorinated water;
- antibacterials and antiseptics;
- dust and soil;
- cement;
- acids and alkalis;
- disinfectants;
- oils used in machines;
- solvents;
- preservatives and perfumes in cosmetics.
Scabies
It is caused by skin infestation with the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which is passed through skin-to-skin contact, typically during sex. Also, these mites can spread quickly in dormitories, nursing homes, camps, and other places where people are crowded together.
Occasionally, an individual can get scabies from contact with an object housing the mite, such as – clothing or bedding.
Note – these parasites can survive outside the human body for 24 to 36 hours.
Risk Factors
People with a tendency to eczema, asthma, and hay fever (allergic rhinitis) develop ICD more easily than other people. In addition, this tendency does run in families.
Moreover, the practice of ear piercing is strongly associated with a nickel allergy.
Risk factors for scabies include:
- immunosuppression;
- sexual contact with multiple partners;
- age under 15 or over 65 years;
- living in close quarters with others who are infected;
- overcrowded living conditions.
Diagnosis
Medical professionals usually diagnose CD from your physical examination and symptoms.
Also, your healthcare professional might use a patch test to determine the potential causes.
Scabies is diagnosed by examining skin scrapings with a microscope.
Treatment
Contact Dermatitis
In most cases, the rash will disappear after exposure to the substance has ended.
But, if your skin is itchy, sore, and scaly, various medical treatments may be suggested to help clear these symptoms. Topical treatment includes cool compresses and corticosteroids.
Scabies
The two most popular treatments are permethrin cream and malathion lotion.
Retreatment may be needed if rash or new burrows continue to appear or if itching continues more than one month after treatment.
To prevent reinfestation, it is recommended that everyone within your household is treated at the same time.
Contact Dermatitis vs Scabies – Differences
Contact dermatitis is a red, itchy rash that is caused by direct contact with a substance or an allergic reaction to it. The two most common variants are:
- irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) – it occurs when the skin is repeatedly exposed to a mild irritant over a long period of time;
- allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) – it is a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to an allergen (about 48–96 hours after exposure).
Scabies is a skin condition that is caused by an infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei. It is typically spread by skin-to-skin contact with a person who has these parasites.
Usual treatments include permethrin or malathion. Hyperinfestation is increasingly recognized in patients with acquired AIDS.
READ THIS NEXT:
Peyronie’s Disease vs. Normal Curvature
Impetigo vs Herpes – Differences
References https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3391944/ https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/scabies https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0021-8707(31)90215-3/abstract
I have a reaction to all of the sensitive free facial cleansers and soaps. Can you think of anything natural that I can cleanse my face with that won’t break me out??
Thanks.
Janet