This article explains what are the differences between Meloxicam and Aleve:
Meloxicam
It is the generic name of a brand medication called Mobic.
The medication belongs to a family of drugs collectively called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that work by blocking the action of cyclooxygenase (COX).
Cyclo-oxygenase is involved in the production of many different chemicals in the body, some of which are known as prostaglandins – the chemicals responsible for causing inflammation and pain in the human body.
Uses
This prescription medication is used to relieve the swelling and pain of rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints) and osteoarthritis.
In addition, it is used occasionally to treat ankylosing spondylitis (a long-term condition in which the spine and other areas of the body become inflamed).
Dosage
The usual initial recommended dose is 0.09 mg/lb body weight (only on the first day of treatment). You should take the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration according to individual response.
It has a plasma half-life of about 20 hours.
Note – your healthcare professional may want to prescribe another drug for you to take along with this one to protect your stomach from irritation.
Side Effects And Precautions
Common side effects may include:
- upset stomach;
- diarrhea;
- gas;
- upper respiratory infection;
- headaches;
- flu-like symptoms;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- edema (an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin and in the cavities of the body);
- heartburn;
- digestive problems;
- stomach pain.
Rare side effects may include:
- cracks in the skin;
- loosening of the skin;
- loss of heat from the body;
- tarry stools;
- severe stomach pain;
- continuing vomiting;
- muscle pain;
- weak pulse;
- red, swollen skin;
- hoarseness;
- scaly skin;
- unpleasant breath odor;
- vomiting of blood that looks like coffee grounds;
- problems with swallowing;
- unusual tiredness;
- irritated eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, lips, face, or tongue;
- a decreased amount of urine;
- fever with or without chills.
Do not take this non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug if you:
- have experienced hives, asthma, nasal polyps, or any type of allergic reaction;
- are allergic to any ingredients of the medication;
- have severely reduced liver function;
- have recently had coronary artery bypass graft surgery;
- have severe uncontrolled heart failure;
- are less than 18 years of age;
- have severely reduced kidney function;
- have inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease);
- have higher than normal levels of potassium in the blood;
- have any bleeding disorders;
- have intestinal ulcers.
Pregnancy
Use of this non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug during pregnancy is not advised unless prescribed by your healthcare provider, particularly if you are 30 or more weeks pregnant.
Drug Interactions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the drugs you take, including non-prescription and prescription drugs and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare professional if you are taking:
- lithium (Eskalith, Lithobid);
- alcohol;
- ACE inhibitors like captopril (Capoten), lisinopril (Prinivil), enalapril (Vasotec), and fosinopril (Monopril);
- cholestyramine (Questran);
- aspirin (Ecotrin) and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxin);
- oxymetazoline;
- cimetidine (Tagamet);
- warfarin (Coumadin);
- dymista;
- cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune);
- methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall);
- Claritin;
- diuretics, like furosemide (Lasix) or thiazides (hydrochlorothiazide).
Aleve
It is the brand name of a drug called naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory product that can be purchased OTC to provide temporary relief of minor pains and aches from conditions like toothaches, arthritis, backaches, and fever (high temperature).
This medication functions to block a hormone-like substance that causes pain and inflammation in the human body, called prostaglandin.
Uses
It is typically used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, inflammation due to muscle aches, arthritis, backache, sprains, strains, headache, minor aches, migraine, toothache, menstrual cramps, dental extractions, minor surgery, and the common cold.
Moreover, it can be used to reduce a high temperature (fever).
Dosage
Take one caplet, tablet, liquid gel, or gelcap every 8 to 12 hours while symptoms last.
For seniors, the usual recommended dose is 1 tablet or capsule every 12 hours.
Side Effects And Precautions
Common side effects may include:
- vomiting;
- stomach pain;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- intestinal gas (excessive flatulence);
- diarrhea;
- constipation.
Note – these side effects are more likely to occur the longer you use the medication or the older you are.
Rare side effects may include:
- bleeding;
- swelling;
- tears in the small intestine, stomach, or large intestine;
- weakness in the legs or arms;
- slurred speech;
- shortness of breath;
- ulcer;
- chest pain.
Alcohol
Consuming more than three alcoholic beverages a day while taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may increase the risk of developing stomach ulcers.
Meloxicam vs Aleve – Which Is Better?
Meloxicam (brand name – Mobic) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is used for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis symptoms by relieving pain and reducing swelling and inflammation.
Aleve (active ingredient – naproxen) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that works by reducing hormones (prostaglandins) which cause inflammation and pain in the human body.
According to a 1996 study conducted at the Eastbourne District General Hospital, Eastbourne, that compared the benefits and side effects of these two NSAIDs, considerably more people discontinued the use due to gastrointestinal adverse effects in the naproxen group.
This is most likely due to a significant increase in serum creatinine and urea and a significant decrease in hemoglobin.
However, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may impact blood pressure, especially among women.
For instance, according to a recent study, women who took “a moderate-high dose” of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs every day were 78% more likely to have hypertension than women who didn’t take the NSAIDs.
7 Natural Anti-Inflammatory Herbs & Foods
#1 Devil’s Claw
This root has been used as a natural treatment for joint pain and backache.
Also, the use of devil’s claw caused a substantial reduction of arthritic inflammation in a group of mice, according to a Japanese study in 2010.
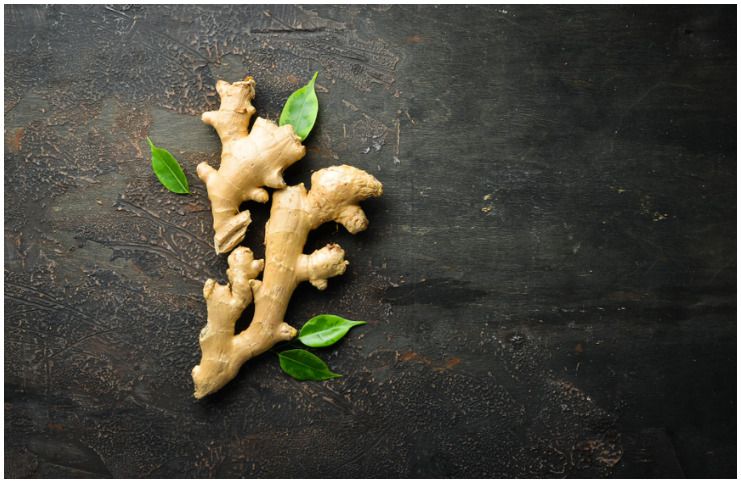
#2 Ginger
A popular spice in Asian food, it has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries.
According to research, ginger has strong natural anti-inflammatory properties, which are similar to prescription medications.
#3 Flax Seeds
One teaspoon of grounded flax seeds per day, substantially decreased pro-inflammatory compounds, as per a 2015 study published in ”Nature.”
#4 Burdock Root
Burdock root is a vegetable that’s native to Europe and northern Asia and Europe.
Burdock root tea improved significantly oxidative stress and inflammatory status in people with degenerative joint disease, according to a study that was issued in the International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.
#5 Turmeric
Curcumin is the main ingredient in this spice and has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
#6 Broccoli
Broccoli is rich in sulforaphane, a phytochemical that has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant attributes.
Sulforaphane is also present in cabbage and cauliflower.
#7 Boswellia Serrata
By turning off the pro-inflammatory cytokines, Boswellia Serrata provides anti-inflammatory activity in areas where there is inflammation.
READ THIS NEXT:
References http://www.medicaldaily.com/fda-aleve-and-other-naproxen-meds-are-safer-your https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2016/11/13/501033431/safety https://www.ajc.com/news/local/common-painkillers-increase-risk-heart-attack