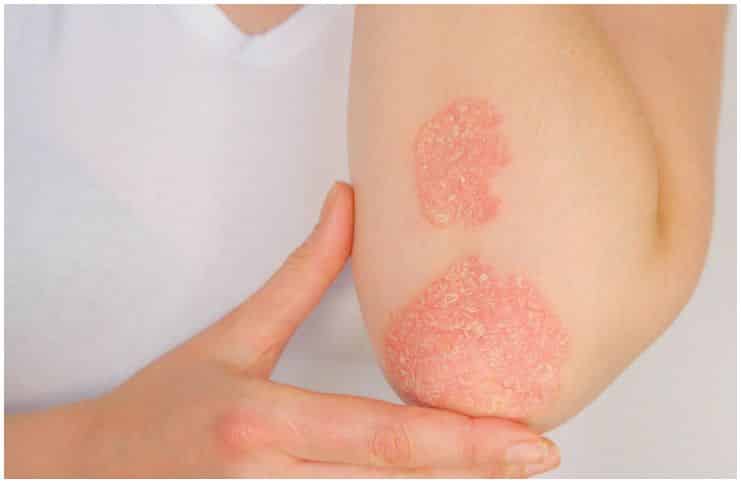
Ringworm (medical term – tinea) is a common fungal infection of the skin. It is not due to a worm. Although it frequently appears on the skin, this infection can also show up on the toenails or fingernails.
Some types of ringworm infection include:
- tinea cruris (“jock itch”);
- tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot”);
- tinea capitis (“herpes tonsurans”).
It can affect people at any age and is estimated that around 20 percent of the population is infected with one form of this infection. However, it is more frequent among children, individuals with poor hygiene habits, and athletes.
Causes
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 40 different species of fungi can cause this infection. These fungi are known as dermatophytes. As per a 2008 study published in the journal Mycoses, tinea corporis is typically caused by M. canis, T. rubrum, or T. tonsurans,
It is possible that these harmful fungi may live for an extended period in the soil, and humans and animals can contract them after direct contact with this soil.
Risk Factors
The following risk factors either increase the chances of developing this skin infection or make the symptoms considerably worse:
- drugs which lower the immune system as well as patients with HIV or AIDS;
- age, especially children younger than 15. This condition is frequently spread among children and by sharing items that may not be clean;
- sharing towels or clothing with infected people;
- wearing tight clothing, making conditions ideal for the fungus to thrive;
- contact sports, particularly where human-to-human contact is the main part of the activity;
- hyperhidrosis, abnormally excessive sweating which is not related to physical exercise or heat. About 3 percent of the people in the United States suffer from this condition;
- being close to infected animals or people;
- living in warm climates.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- nail problems which present themselves with discoloration and crumbling nails;
- scalp problems;
- red scaly patches that have sharply-defined edges;
- red, scaly patches which may blister.
Diagnosis
Healthcare specialists can diagnose this skin infection on sight, plus, they may take a skin scraping. Also, a specialized agar plate is used to culture and identify the fungi causing the infection.
Treatment
Your healthcare provider may recommend an OTC drug. In addition, to avoid spreading the condition to others:
- stay away from gyms and community pools until your infection heals;
- wash clothes and towels in soap and hot water;
- do not share clothing, towels, or hairbrushes;
- keep your hair, skin, and nails dry and clean.
Psoriasis
It is a chronic autoimmune disease wherein skin cells tend to build up much faster, leading to inflammation and scaling in the form of swelling, pain, redness, and heat.
There are roughly 150,000 new patients per year in the US. In the present day, it affects about 8 million Americans. Worldwide, 3% of the population has this autoimmune disease, according to the IFPA.
Usually, sufferers have their first outbreak between the ages of 15 and 35. People experiencing this condition are at increased risk of depression, heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, cancer, and type 2 diabetes. Also, about 4 in 10 patients have joint inflammation which produces symptoms (joint pain and stiffness) of arthritis.
Total healthcare costs of this autoimmune disease are around $11.40 billion per year.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- stiff and swollen joints;
- pitted or ridged nails;
- burning or soreness of the skin;
- cracked skin which may bleed;
- small scaling spots;
- red patches of skin covered with silvery scales.
Note – although the plaques can be limited to a few small areas, they can spread to any area of your skin. Most patients go through cycles, causing problems for a few months before easing.
Causes
Like other autoimmune diseases, the exact cause is not completely understood, however, doctors believe it’s a combination of environmental triggers and genetic predisposition.
According to the data, about 10 percent of the American population has the genes to potentially develop this autoimmune disease. More importantly, this condition cannot be passed from person to person and is not contagious, although, it can occur in members of the same family.
Risk factors that can increase the chances of this disease include:
- A cold weather since during winter, people usually spend more time indoors and get less sun.
- Skin irritations, like – scratches, cuts, rashes, sunburns can make this condition more likely to occur.
- A diet rich in dairy products.
- Emotional stress can have a negative effect on the body’s immune system.
- Certain drugs, such as – beta-blockers for hypertension, lithium, and medicines used to prevent malaria.
- Being obese or overweight.
- Infections, including – colds and strep throat.
Diagnosis
There are no special blood tests to diagnose this disease. A dermatologist typically examines the affected skin.
Treatment
Treatments usually fall into 3 main categories:
- injected and oral drugs – they work by reducing the production of the skin cells;
- phototherapy – during this treatment, the affected skin is exposed to some specific types of ultraviolet light;
- ointments and creams which are applied to the skin.
Natural Remedies
Natural remedies include:
- Eat foods high in fiber — increasing your intake of dietary fiber can help to maintain your digestive system healthy, which actually keeps your natural detoxification processes on track and helps avoid constipation.
- Capsaicin – it is found in hot pepper and has potent anti-inflammatory attributes. You can use a cream which contains it or you can eat the hot pepper.
- Reduce your stress – it may help relieve the itch and pain of the plaques. Meditation is one the best methods as well as healthy sleeping patterns. In addition, Tai Chi and yoga may improve your condition.
- Aloe vera gel is known to help heal skin wounds. Moreover, this gel may help reduce scaling, redness, and inflammation caused by this autoimmune disease.
- Vitamin D – spend some time outside to have high levels of vitamin D.
- Turmeric – it is a spice with anti-inflammatory properties which help minimize the symptoms. It is best consumed in combination with black pepper.
- Apple cider vinegar – it may help relieve scalp itch due to this condition. It is recommended to purchase organic ACV.
Ringworm vs Psoriasis – Differences
Ringworm is a fungal infection that develops on the top layer of the skin. The infection initially appears with red patches and later spreads to other parts of your body. It is highly contagious. Even other mammals, including dogs and cats, can easily transfer the fungi to humans.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disease. The impact of this chronic condition on people’s lives can be immense. It is characterized by alternate periods with outbreaks and good periods. There is no cure for this condition, however, there are many allopathic and natural treatments that can help to keep this disease under control. It is not contagious.
Images credit – Shutterstock & Getty
READ THIS NEXT: Interesting Facts About Rosacea
References https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1590528/ https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-ringworm-infections-caused- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriasis/diagnosis-treatmen